Graphs - Implementing Dijkstras Algorithm (Shortest Path) in Java - Part Three
Now that we have finished writing our Shortest Path algorithm let’s write some code to test it so we can see it in action. To do this we will write a constructor for our DjikstrasAlgoExample class that makes a graph and prints out all of the shortest paths amongst the nodes.
Before we start here’s an image depicting the graph we will test Dijkstra’s Algorithm on: 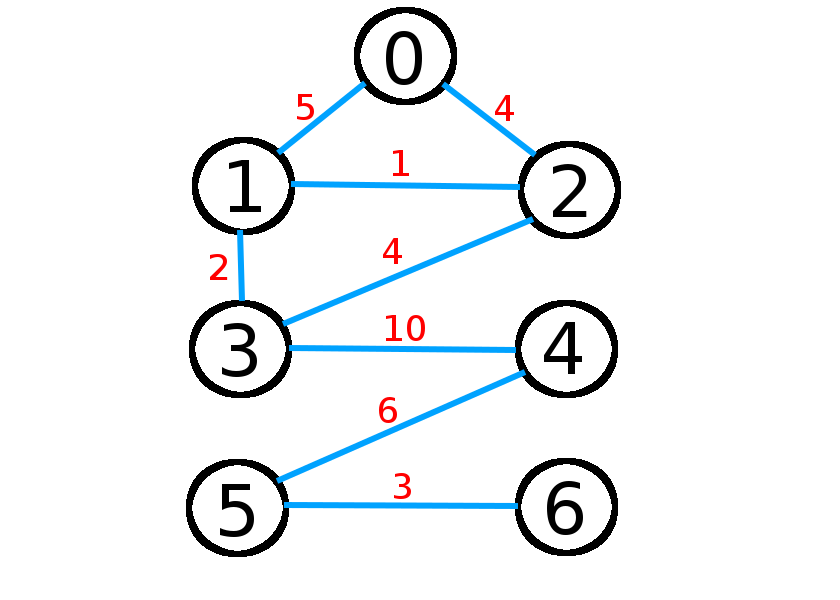
Declare the constructor:
Declare the seven nodes to be held in the graph. Each node is named n“the number it contains” to allow us to easily remember which node is which.
Node<Integer> n0 = new Node<Integer>(0);
Node<Integer> n1 = new Node<Integer>(1);
Node<Integer> n2 = new Node<Integer>(2);
Node<Integer> n3 = new Node<Integer>(3);
Node<Integer> n4 = new Node<Integer>(4);
Node<Integer> n5 = new Node<Integer>(5);
Node<Integer> n6 = new Node<Integer>(6);Put each node into our graph:
graph.put(n0.getIndex(), n0);
graph.put(n1.getIndex(), n1);
graph.put(n2.getIndex(), n2);
graph.put(n3.getIndex(), n3);
graph.put(n4.getIndex(), n4);
graph.put(n5.getIndex(), n5);
graph.put(n6.getIndex(), n6);Add the edges between each of the nodes in our graph:
n0.addEdge(n1, 5);
n0.addEdge(n2, 4);
n1.addEdge(n3, 2);
n1.addEdge(n2, 1);
n2.addEdge(n3, 4);
n3.addEdge(n4, 10);
n4.addEdge(n5, 6);
n5.addEdge(n6, 3);Finally print out the shortest path between node 0 and each of the rest of the nodes:
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
System.out.println("Dijkstra's algorithm test:");
System.out.println("n0 -> n1: " + getShortestPath(n0, n1));
System.out.println("n0 -> n2: " + getShortestPath(n0, n2));
System.out.println("n0 -> n3: " + getShortestPath(n0, n3));
System.out.println("n0 -> n4: " + getShortestPath(n0, n4));
System.out.println("n0 -> n5: " + getShortestPath(n0, n5));
System.out.println("n0 -> n6: " + getShortestPath(n0, n6));The finished constructor is as follows:
public DijkstrasAlgoExample() {
Node<Integer> n0 = new Node<Integer>(0);
Node<Integer> n1 = new Node<Integer>(1);
Node<Integer> n2 = new Node<Integer>(2);
Node<Integer> n3 = new Node<Integer>(3);
Node<Integer> n4 = new Node<Integer>(4);
Node<Integer> n5 = new Node<Integer>(5);
Node<Integer> n6 = new Node<Integer>(6);
graph.put(n0.getIndex(), n0);
graph.put(n1.getIndex(), n1);
graph.put(n2.getIndex(), n2);
graph.put(n3.getIndex(), n3);
graph.put(n4.getIndex(), n4);
graph.put(n5.getIndex(), n5);
graph.put(n6.getIndex(), n6);
n0.addEdge(n1, 5);
n0.addEdge(n2, 4);
n1.addEdge(n3, 2);
n1.addEdge(n2, 1);
n2.addEdge(n3, 4);
n3.addEdge(n4, 10);
n4.addEdge(n5, 6);
n5.addEdge(n6, 3);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
System.out.println("Dijkstra's algorithm test:");
System.out.println("n0 -> n1: " + getShortestPath(n0, n1));
System.out.println("n0 -> n2: " + getShortestPath(n0, n2));
System.out.println("n0 -> n3: " + getShortestPath(n0, n3));
System.out.println("n0 -> n4: " + getShortestPath(n0, n4));
System.out.println("n0 -> n5: " + getShortestPath(n0, n5));
System.out.println("n0 -> n6: " + getShortestPath(n0, n6));
}The output of running the code is:
-------------------------------------
Dijkstra's algorithm test:
n0 -> n1: 5
n0 -> n2: 4
n0 -> n3: 7
n0 -> n4: 17
n0 -> n5: 23
n0 -> n6: 26The finished DijkstrasAlogExample class is as follows:
package com.spartanengineer.datastructures;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Set;
import javafx.util.Pair;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class DijkstrasAlgoExample {
private static int nodeIndex = 0;
// undirected graph example
private class Node<U> {
private U data;
private Map<Node<U>, Integer> edges;
private int index = -1;
public Node(U data) {
this.data = data;
edges = new HashMap<Node<U>, Integer>();
this.index = nodeIndex;
nodeIndex += 1;
}
public U getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(U data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Map<Node<U>, Integer> getEdges() {
return edges;
}
public void setEdges(Map<Node<U>, Integer> edges) {
this.edges = edges;
}
public int getIndex() {
return index;
}
public void setIndex(int index) {
this.index = index;
}
/**
* Add an undirected edge, will replace an already existing edge between the two nodes
*/
public void addEdge(Node<U> node, int weight) {
edges.put(node, weight);
if(!node.getEdges().containsKey(this)) {
node.addEdge(this, weight);
} else {
if(node.getEdges().get(this) != weight) {
node.addEdge(this, weight);
}
}
}
}
// Used to allow our priority queue to order edge pairs correctly
private class EdgePairComparator implements Comparator<Pair<Node<Integer>, Integer>> {
@Override
public int compare(Pair<Node<Integer>, Integer> o1, Pair<Node<Integer>, Integer> o2) {
return o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue());
}
}
private Map<Integer, Node<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
public DijkstrasAlgoExample() {
Node<Integer> n0 = new Node<Integer>(0);
Node<Integer> n1 = new Node<Integer>(1);
Node<Integer> n2 = new Node<Integer>(2);
Node<Integer> n3 = new Node<Integer>(3);
Node<Integer> n4 = new Node<Integer>(4);
Node<Integer> n5 = new Node<Integer>(5);
Node<Integer> n6 = new Node<Integer>(6);
graph.put(n0.getIndex(), n0);
graph.put(n1.getIndex(), n1);
graph.put(n2.getIndex(), n2);
graph.put(n3.getIndex(), n3);
graph.put(n4.getIndex(), n4);
graph.put(n5.getIndex(), n5);
graph.put(n6.getIndex(), n6);
n0.addEdge(n1, 5);
n0.addEdge(n2, 4);
n1.addEdge(n3, 2);
n1.addEdge(n2, 1);
n2.addEdge(n3, 4);
n3.addEdge(n4, 10);
n4.addEdge(n5, 6);
n5.addEdge(n6, 3);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
System.out.println("Dijkstra's algorithm test:");
System.out.println("n0 -> n1: " + getShortestPath(n0, n1));
System.out.println("n0 -> n2: " + getShortestPath(n0, n2));
System.out.println("n0 -> n3: " + getShortestPath(n0, n3));
System.out.println("n0 -> n4: " + getShortestPath(n0, n4));
System.out.println("n0 -> n5: " + getShortestPath(n0, n5));
System.out.println("n0 -> n6: " + getShortestPath(n0, n6));
}
public int getShortestPath(Node<Integer> start, Node<Integer> end) {
//keeps track of the distance between this node and every other node
Map<Integer, Integer> distances = new HashMap<>();
for(Node<Integer> n : graph.values())
distances.put(n.getIndex(), Integer.MAX_VALUE);
//keeps track of which nodes we have visited
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<Integer>();
//declare a priority queue which will be used to help find the shortest path to each node
PriorityQueue<Pair<Node<Integer>, Integer>> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new EdgePairComparator());
//initially load the priority queue with the start node (as that is where we start!!!)
Pair<Node<Integer>, Integer> startPair = new Pair<>(start, 0);
queue.add(startPair);
//when the queue is empty we will have found the shortest distance from the start node to all other nodes
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
//the pair at the front of the queue will be the current node to visit
Pair<Node<Integer>, Integer> pair = queue.remove();
Node<Integer> node = pair.getKey();
Integer weight = pair.getValue();
int nodeIndex = node.getIndex();
if(weight < distances.get(nodeIndex)) {
//if a shorter path has been found then update the distance
distances.put(nodeIndex, weight);
}
//visit all the adjacent nodes to the node currently being visited
if(!visited.contains(nodeIndex)) {
visited.add(nodeIndex); //mark off this node so that we don't have to visit it again
Map<Node<Integer>, Integer> edges = node.getEdges();
for(Node<Integer> edgeNode : edges.keySet()) {
int edgeWeight = edges.get(edgeNode);
Pair<Node<Integer>, Integer> edgePair = new Pair<>(edgeNode, weight+edgeWeight);
queue.add(edgePair);
}
}
}
return distances.get(end.getIndex());
}
}