Graph
A graph is a data structure that contains a set of vertices (or nodes). This version of a graph (from the field of graph theory: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graph_(discrete_mathematics)) is not to be confused with the graph of a function (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graph_of_a_function). Each node (AKA vertex) in a graph contains data associated with that particular node as well as references to each node that it is connected to (ie shares an edge with). An edge is a link between two nodes. A graph may directed or undirected. In a directed graph each edge goes in one direction (like a one way street) from a node to another. In an undirected graph each edge does not have a direction (like a two way street). Edges may also be weighted. What it means for an edge to be weighted is that it has a numerical value associated with each edge. These values correspond to the distance between the two nodes linked by the edge.
A visual representation of an undirected graph is as follows: 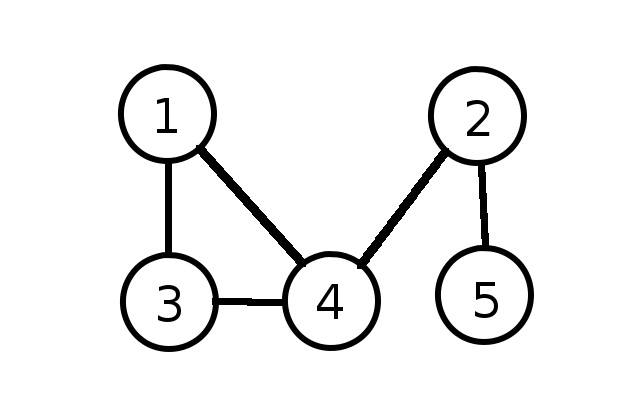
A visual representation of a directed graph is as follows: 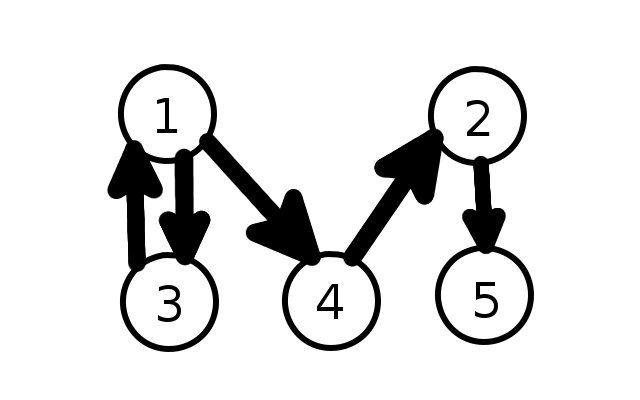
Advantages/Disadvantages of Graphs:
Advantages:
- quintessential data structure for solving certain problems (ie finding the shortest path between two nodes, it is the data structure behind things like Google maps)
- many problems can be restated as a graph problem
- easy to visualize a graph (as long as the data set is small)
- trees can be thought of as a limited version of a directed graph
Disadvantages:
- slow to search through a graph
- uses a lot of memory compared to other data structures
- an advanced data structure that is difficult to write algorithms for, many beginners don’t understand graphs very well at all
- algorithms to deal with graphs can often be slow
- difficult to visualize a large graph dataset
- many graph theory problems can be brutally difficult