Linked Lists
A linked list is a data structure that can be used to store data. It is is essentially a collection of nodes. Each node in a linked list contains the data object to be stored as well as a reference (link) to the next node in the list. If the node is the last in the list then it’s next node is set to nothing. The resulting structure conceptually resembles a chain. The head node in the linked list is stored in the list itself.
Here’s an image depicting what a linked list looks like conceptually: 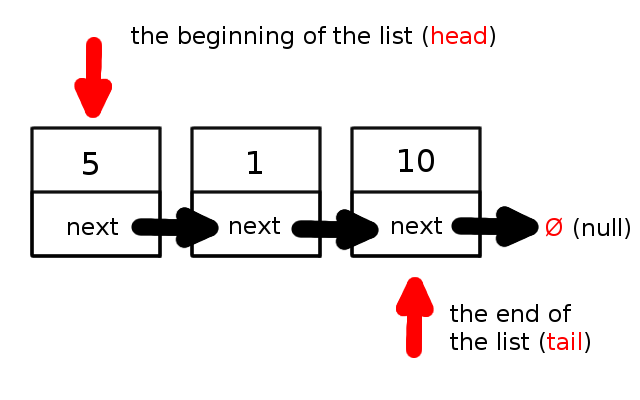
Advantages/Disadvantages of Linked Lists:
Advantages:
- resizable
- fast to add to the list
- fast to delete an element from list
- useful for implementing queues/stacks
- only stores as many nodes as needed
- easy to remove/insert a node at any position in the list
Disadvantages:
- slow search
- slow to access an index
- sorting is much more complicated then an array
- uses slightly more memory then an array (because of the need to store the reference to the next node in each node)
- no way to iterate backwards through the elements (this is solved in a doubly linked list, but comes with the cost of more memory used)
Singly vs Doubly Linked List
Singly A singly linked list is what has been described. It is a linked list in which each node contains a data element as well as a reference to the next node. This allows us to iterate forwards through the linked list, but not backwards.
Doubly A doubly linked list is a linked list in which each node contains a data element as well as a reference to both the next node and the previous node. This gives us the extra ability to iterate backwards (as well as forwards) through the linked list. This extra ability comes with the cost of the list taking up more space in memory. The list will take up more space in memory because each node in the list now requires an extra pointer.